


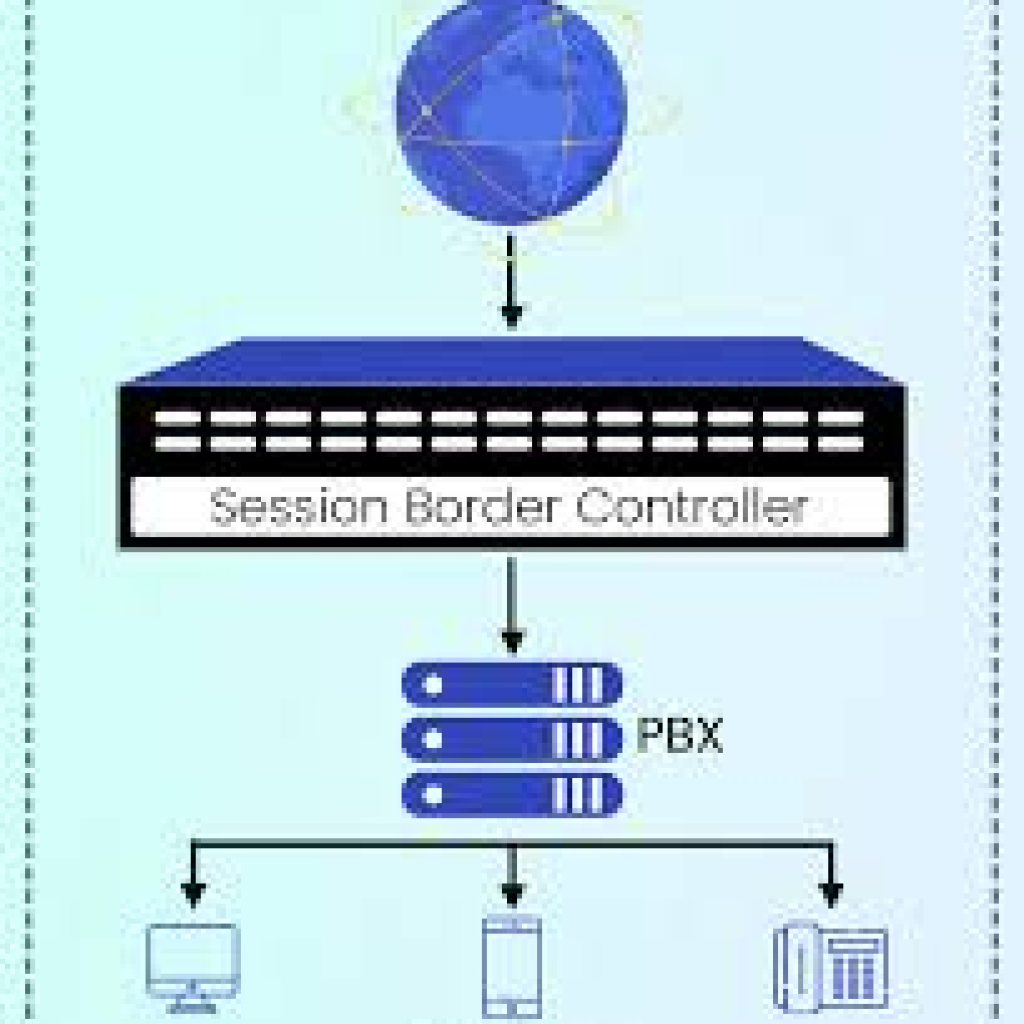
IP-PBX (core server) — the heart that routes calls and runs voicemail, IVR, auto-attendant and call queues. (On-prem hardware or virtual appliance.)
SIP Trunks / Telephony Gateways — the connection to the PSTN (phone company). Can be SIP trunks (recommended) or PRI/analog gateways for fallback.
IP Phones / Softphones — desk phones (IP keyphones) + smartphone/desktop apps for remote staff.
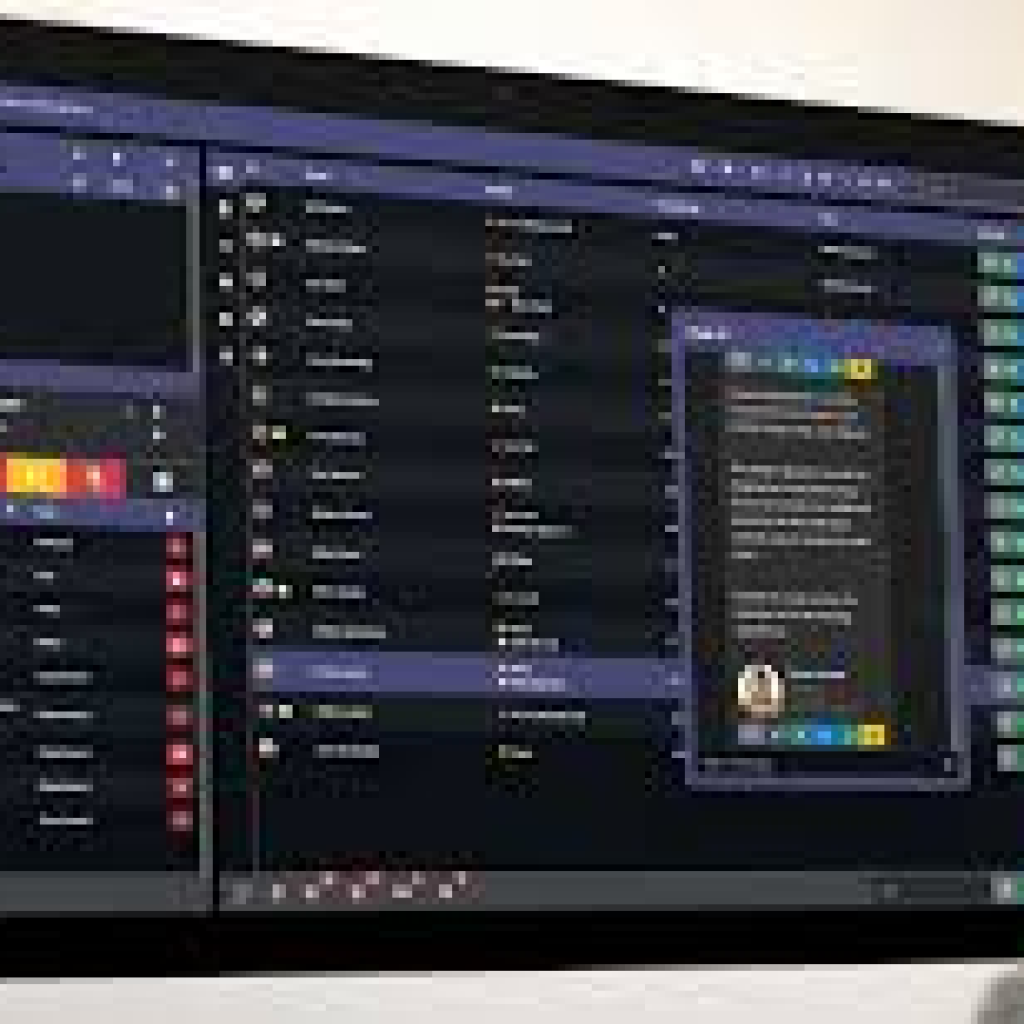
Operator console / Reception dashboard — visual call-board for receptionist showing caller, queue length, hold times, transfer buttons.
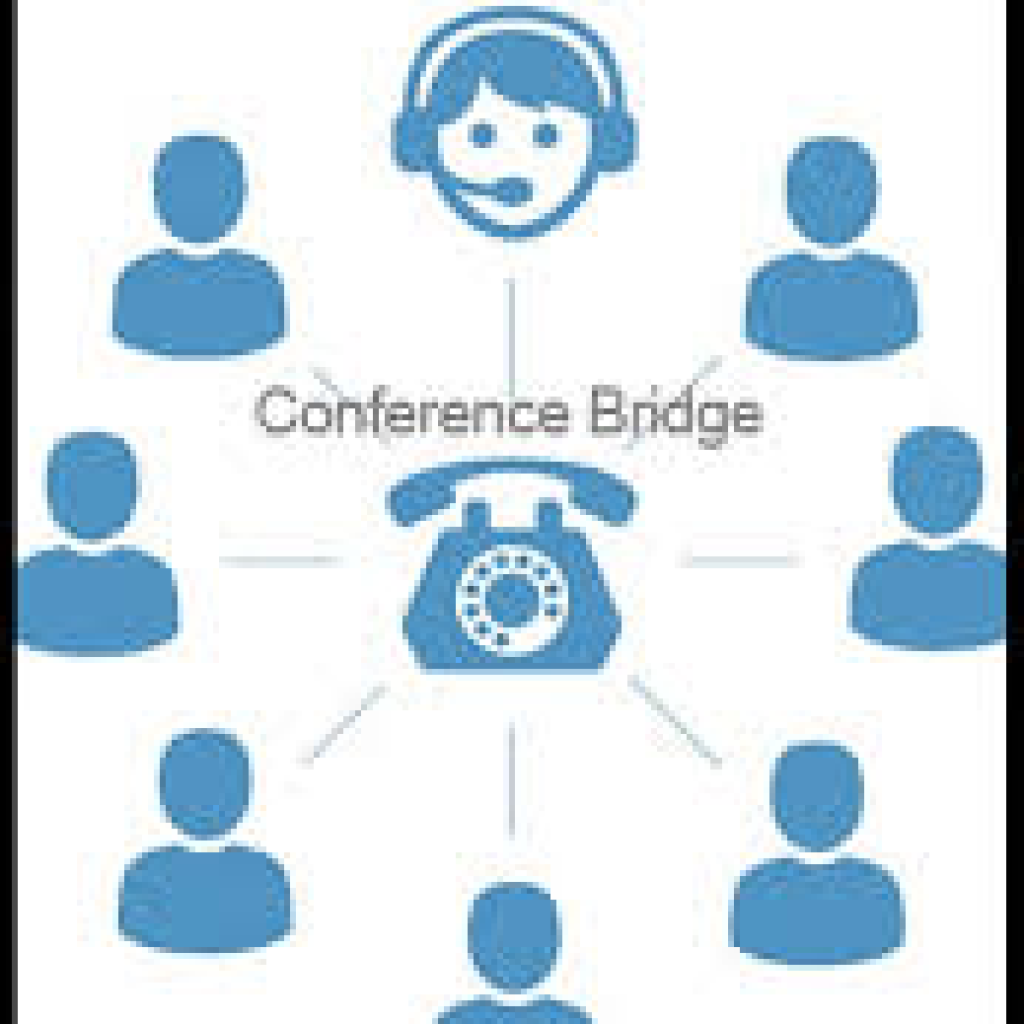



Conference bridge — built-in or external conferencing module for multi-party audio (and optionally video/web meetings).
Call Recording & Call Center features — recording, wallboard, SLA reports, call logs.
SBC (Session Border Controller) — security layer to protect VoIP from attacks and NAT traversal.
Network infrastructure — PoE switches, VLANs, QoS, firewall, UPS.
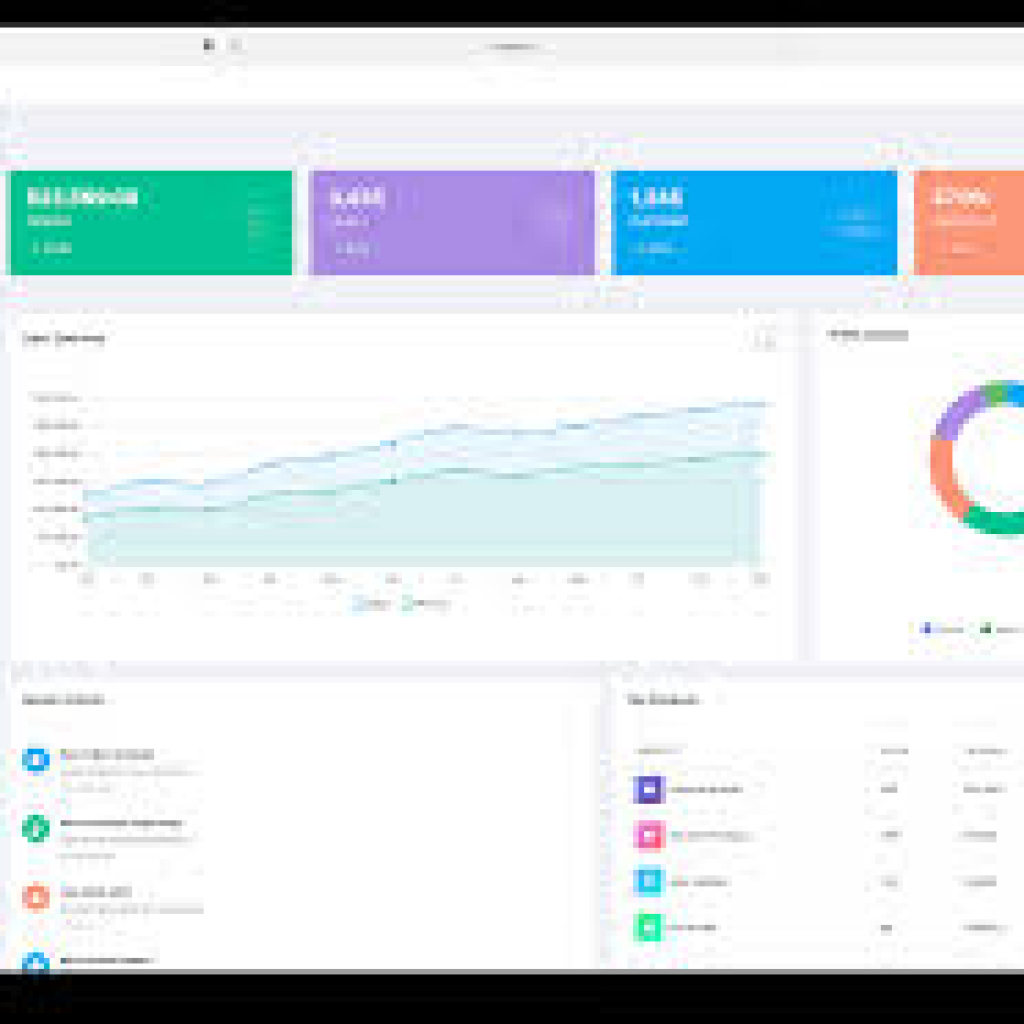



Management Dashboard — web UI with live status, call analytics, reports and provisioning tools.
Extensions for 150 users — Each staff gets an extension (like an internal phone number). Internal calls are free and fast.
Auto-Attendant (IVR) — “Welcome, press 1 for Sales, 2 for Support” — automated menu that routes callers without a human operator.
- IP-PBX appliance (Main) — e.g., Grandstream UCM6304 / Yeastar S300 (sized for ≥150 users & 30–100 concurrent calls).
What it does: routes every call, runs features (IVR, voicemail, conferencing), stores call logs.
